The Viking Age was a time of great artistic expression and innovation in Northern Europe. Viking art and architecture were highly influential in shaping the cultural identity of the Norse people and their impact can still be seen today in the surviving artifacts and buildings from the era. This blog post will explore the styles and techniques of Viking art and architecture, highlighting their significance and legacy.

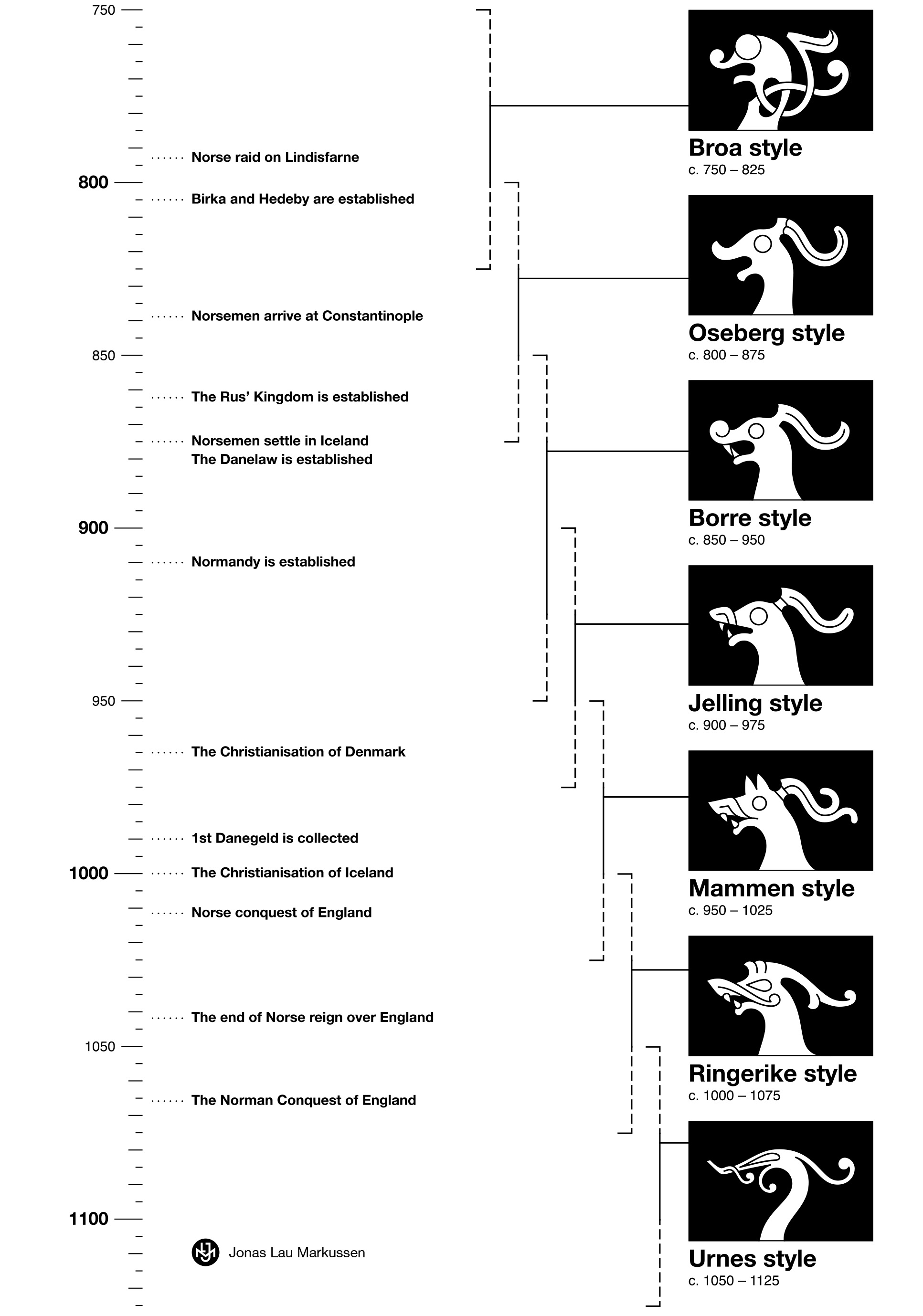
Styles of Viking Art Viking art was highly symbolic and often featured intricate designs and patterns. The most common motifs found in Viking art include animals, such as dragons, serpents, and wolves, as well as geometric shapes and knots. These motifs were often combined to create complex and beautiful designs, which were used to decorate a wide range of objects, including weapons, jewelry, and everyday items such as combs and spoons.
The two most prominent styles of Viking art are the Oseberg style and the Borre style. The Oseberg style is characterized by intricate and detailed animal motifs, while the Borre style features more abstract and stylized designs. Both styles are highly ornamental and were used in the decoration of everything from ship prows to brooches.
Techniques of Viking Art Viking artists were highly skilled and used a range of techniques to create their works. One of the most common techniques used in Viking art was filigree, which involves the use of thin strips of metal twisted and soldered together to create intricate designs. Another popular technique was repoussé, which involves hammering metal from the reverse side to create a raised design on the front.
Viking Architecture Viking architecture was also highly innovative, with the Vikings developing their own distinctive style of building. Viking buildings were typically made from timber, with thatched roofs and turf walls. The most iconic Viking buildings are the longhouses, which were used as communal living spaces and for hosting feasts and other events.
One of the most notable examples of Viking architecture is the Urnes Stave Church in Norway, which is a UNESCO World Heritage site. The church is built in the traditional Viking style, with intricately carved wooden decorations and a steeply pitched roof. The church is a testament to the skill and ingenuity of Viking builders and has inspired countless imitations in the centuries since its construction.
Conclusion Viking art and architecture were highly innovative and influential, and their legacy can still be seen in the surviving artifacts and buildings from the era. From the intricate animal motifs of the Oseberg style to the innovative timber buildings of the Vikings, their artistic achievements continue to inspire and fascinate people today.
Works Cited:
- Graham-Campbell, James, and David M. Wilson. The Viking World. Routledge, 2013.
- Jesch, Judith. Viking Art. Thames & Hudson, 2013.
- Jones, Gwyn. A History of the Vikings. Oxford University Press, 1984.
- Sawyer, Peter. The Oxford Illustrated History of the Vikings. Oxford University Press, 1997.




Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.